Abstract
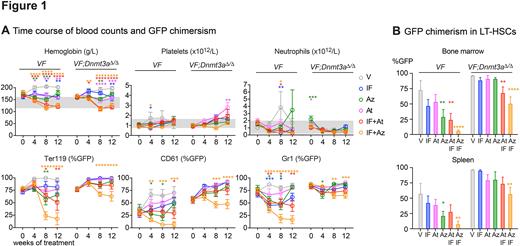
Pegylated interferon alpha (IF) can induce molecular remissions in subset of JAK2-V617F-positive MPN patients by targeting long-term hematopoietic stem cells (LT-HSCs). Patients with additional somatic mutations in genes involved in LT-HSC self-renewal have been reported to have poorer responses to IF. We found that loss of Dnmt3a increases competitiveness and self-renewal of JAK2-V617F-positive LT-HSCs and confers resistance to IF treatment in MPN mouse models and in HSCs and progenitor cells from MPN patients. Here we examined whether the resistance of double mutant JAK2-V617F;Dnmt3aΔ/Δ hematopoietic cells to IF can be overcome by addition of arsenic trioxide (At), or 5-azacytidine (Az). To test the effects of the combination treatments in vivo, we generated cohorts of mice expressing JAK2-V617F (VF) alone, or in combination with a homozygous deletion of the Dnmt3a gene (Dnmt3aΔ/Δ). We used bone marrow cells from VF or VF;Dnmt3aΔ/Δ mice that express a GFP reporter gene mixed with a 10-fold excess of bone marrow cells from a wildtype (WT) mouse to perform competitive transplantations into lethally irradiated WT recipient mice. After 7 weeks, recipient mice were randomized into 6 treatment groups including a vehicle control group. These mice were treated for 12 weeks with IF (25µg/kg; s.c. once per week), At (5mg/kg; i.p. every second day), or Az (2mg/kg; i.p. daily for two weeks followed by a break of 2 weeks), or combinations of IF+At and IF+Az (Figure 1). Peripheral blood parameters were normalized by At and Az treatment arms in both single-mutant and double-mutant mice (Figure 1A). Spleen and liver weight was decreased in all treatment groups and genotypes, except in VF;Dnmt3aΔ/Δ mice treated with IF alone, which showed a trend towards increased spleen and liver weights. Expression of GFP allowed us to follow the contribution of cells derived from the VF or VF;Dnmt3aΔ/Δ donor mice, respectively. In VF recipient mice, a pronounced decrease in GFP chimerism of peripheral blood lineages was observed in the groups treated with a combination of IF+At, or IF+Az (Figure 1A). LT-HSC from bone marrow and spleen showed reduction in GFP chimerism upon treatment with Az alone, compared to vehicle and further reduction below 10% was observed in combination of Az and IF (Figure 1B). Double-mutant VF;Dnmt3aΔ/Δ recipient mice remained resistant to the single agent regiments, but showed a significant reduction of GFP chimerism in peripheral blood and in LT-HSCs when treated with a combination of IF+Az and to a lesser degree also when treated with IF+At (Figure 1B). Thus, a combination of pegIFNa with 5-azacytidine is a promising approach to target MPN cells carrying mutations in JAK2 and Dnmt3a genes that could be also considered as a treatment option for therapy-resistant forms of MPN in patients carrying JAK2-V617F and loss-of-function DNMT3A mutations.
Disclosures
Skoda:BMS/Celgene and Novartis: Honoraria; Ajax Therapeutics: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal